How To Make Laminar Flow
What is laminar menses?
What is laminar flow?
Laminar period is fundamental to the operating principle of Alicat differential pressure instruments, enabling them to output highly accurate mass flow rates beyond very wide measurement and control ranges.
In this article, we briefly discuss different menstruation types with a focus on laminar flow.
Turbulent, laminar, and transitional period
When flowing through a channel, a fluid tin be described as either turbulent, laminar, or transitional.
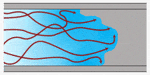
Turbulent menstruum through a aqueduct
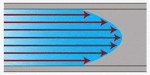
Laminar menstruation through a aqueduct
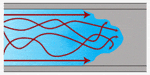
Transitional flow through a aqueduct
Turbulent menstruation
Turbulent catamenia is the most common kind of flow. This type of flow is chaotic, and its pressure and velocity vary significantly throughout the flow channel. Turbulent menses does not exist in uniform layers, simply rather mixes throughout the flow channel.
It is characterized by a pressure level drop that is proportional to the square of the velocity of the menses.
Laminar menstruum
Laminar flow, also called streamline flow, is smoothen and layered. It is more than probable to occur at lower menses rates, in small flow channels, and with high viscosity fluids. Laminar flow exhibits a uniform velocity contour across a channel. The fluid flowing near the heart of the aqueduct moves with the highest velocity, and predictably decreases as it approaches the channel walls.
At laminar catamenia conditions, there is a linear relationship between pressure drib and flow velocity.
Transitional menstruation
Transitional menstruum exhibits characteristics of both laminar and turbulent flow. Fluid catamenia is laminar at the edges of the channel, but turbulent at the center. The exact proportion of turbulent to laminar menstruation can vary from almost entirely laminar to nearly all turbulent.
Information technology is very difficult to accurately summate a differential pressure reading using transitional flow, as the pressure driblet is proportional to an ill-defined polynomial.
How do y'all know if flow is laminar?
In the late 1800s, Osbourne Reynolds came upward with the Reynolds number (Re). This number can exist used to predict the flow type under a sure set of conditions.
Reynolds number (Re)
Re = 2ρVr/η
ρ = Fluid density; V = Average fluid velocity; r = Hydraulic radius of the flow channel; η = Absolute viscosity of the fluid
Reynolds numbers by and large* fall into ranges that indicate whether menses is laminar, turbulent, or transitional.
- Laminar flow: Re < 2,000
- Transitional menstruum: 2000 < Re < four,000
- Turbulent menstruum: Re > four,000
*These numbers may be radically affected by surface finishes of channel walls.
Converting turbulent menses to laminar flow
To reduce the Reynolds number and obtain laminar flow, you tin reduce flow velocity or catamenia channel dimensions. You can likewise menstruum the fluid with a lower density or higher viscosity.
The video below demonstrates how an Alicat device converts turbulent flow into laminar flow.
Want content similar this delivered to your inbox once a month?
Sign up for our newsletter
Source: https://www.alicat.com/knowledge-base/what-is-laminar-flow/
Posted by: burnettannold.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Make Laminar Flow"
Post a Comment